We are a team of dentists, consultants and assistants who work together to make sure you get the treatment you need at the appropriate time.
Make Your Appointment Dentist
Dinamik Dental Clinic
Our treatments
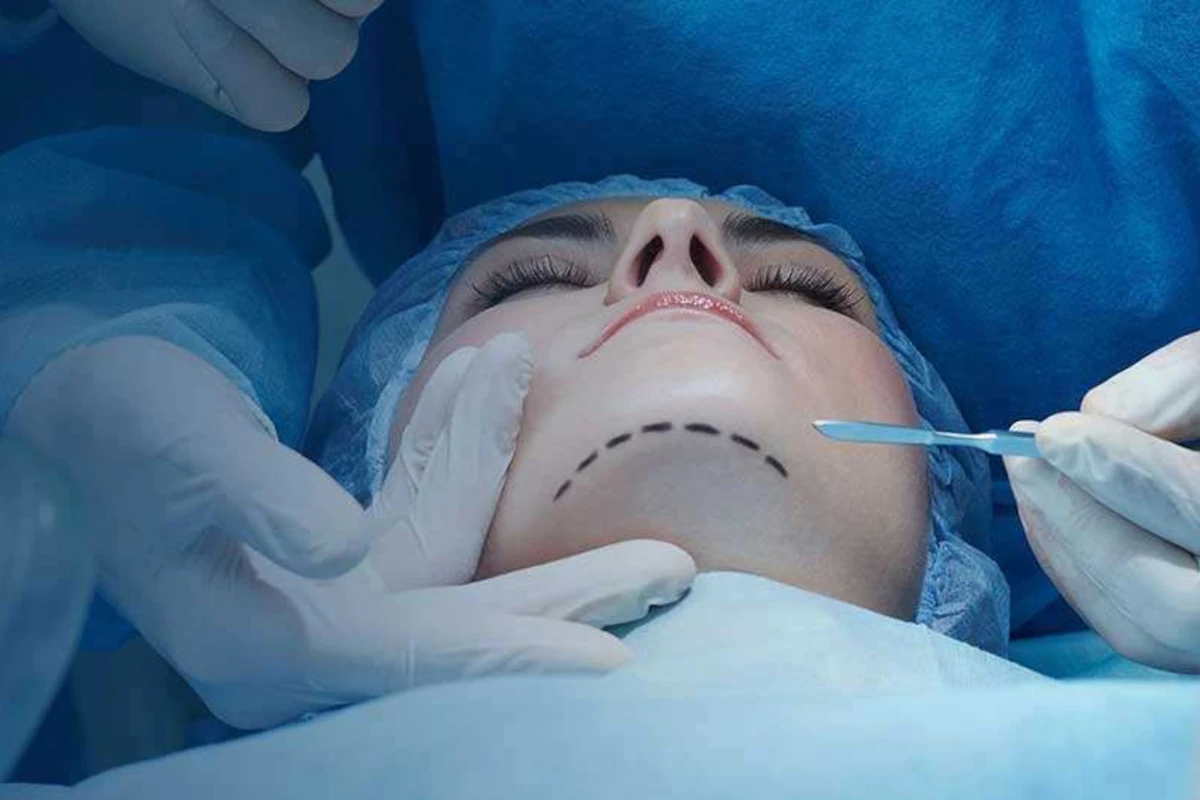
Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
Oral, dental and maxillofacial surgery procedures accompanied by experts in our clinic.
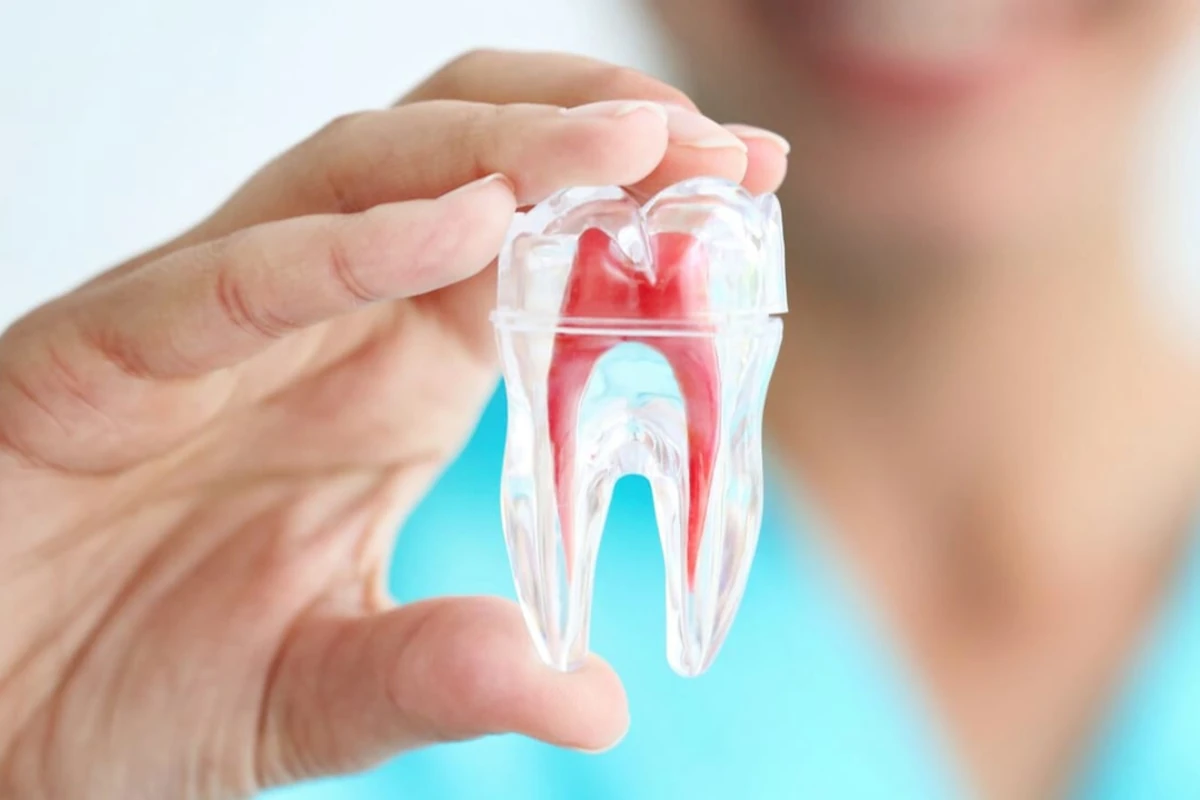
Endodontic Treatments
We welcome you to our clinic for endodontic treatment procedures with our root canal treatment specialist.
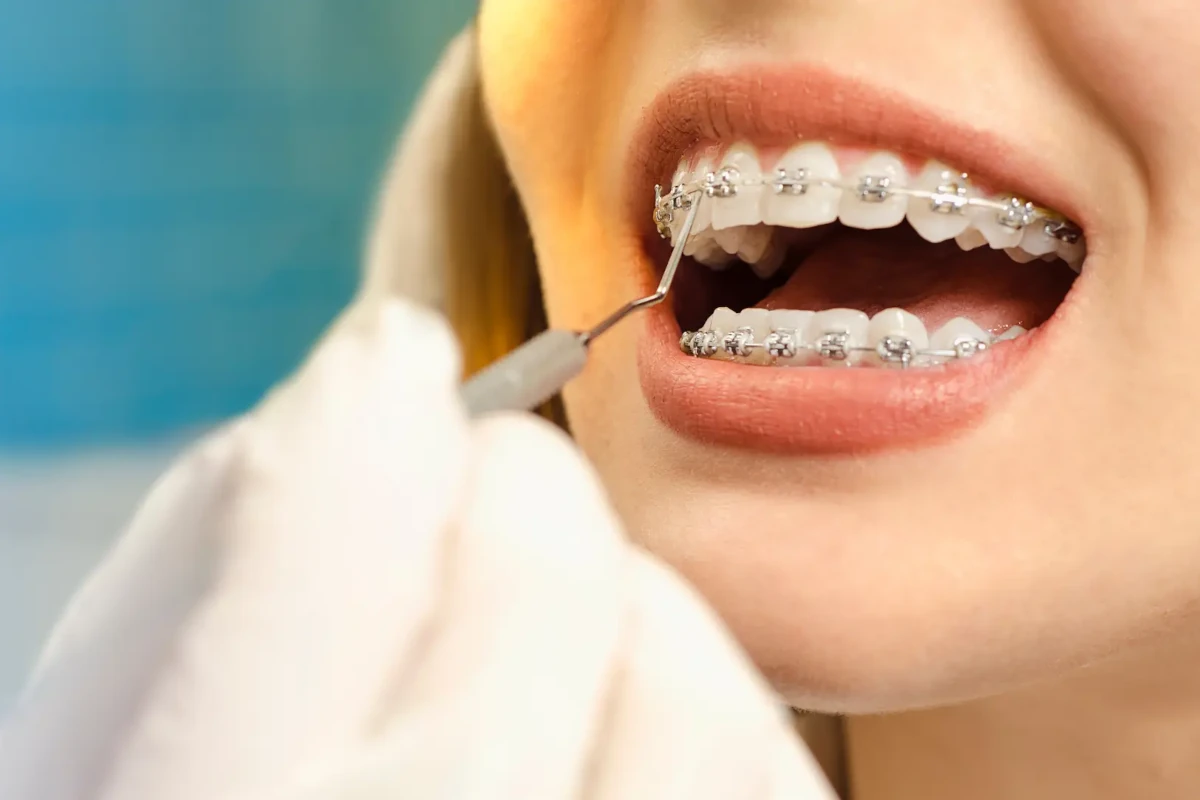
Orthodontic Treatments
We are at the service of our valued patients in our clinic with our orthodontic specialist.
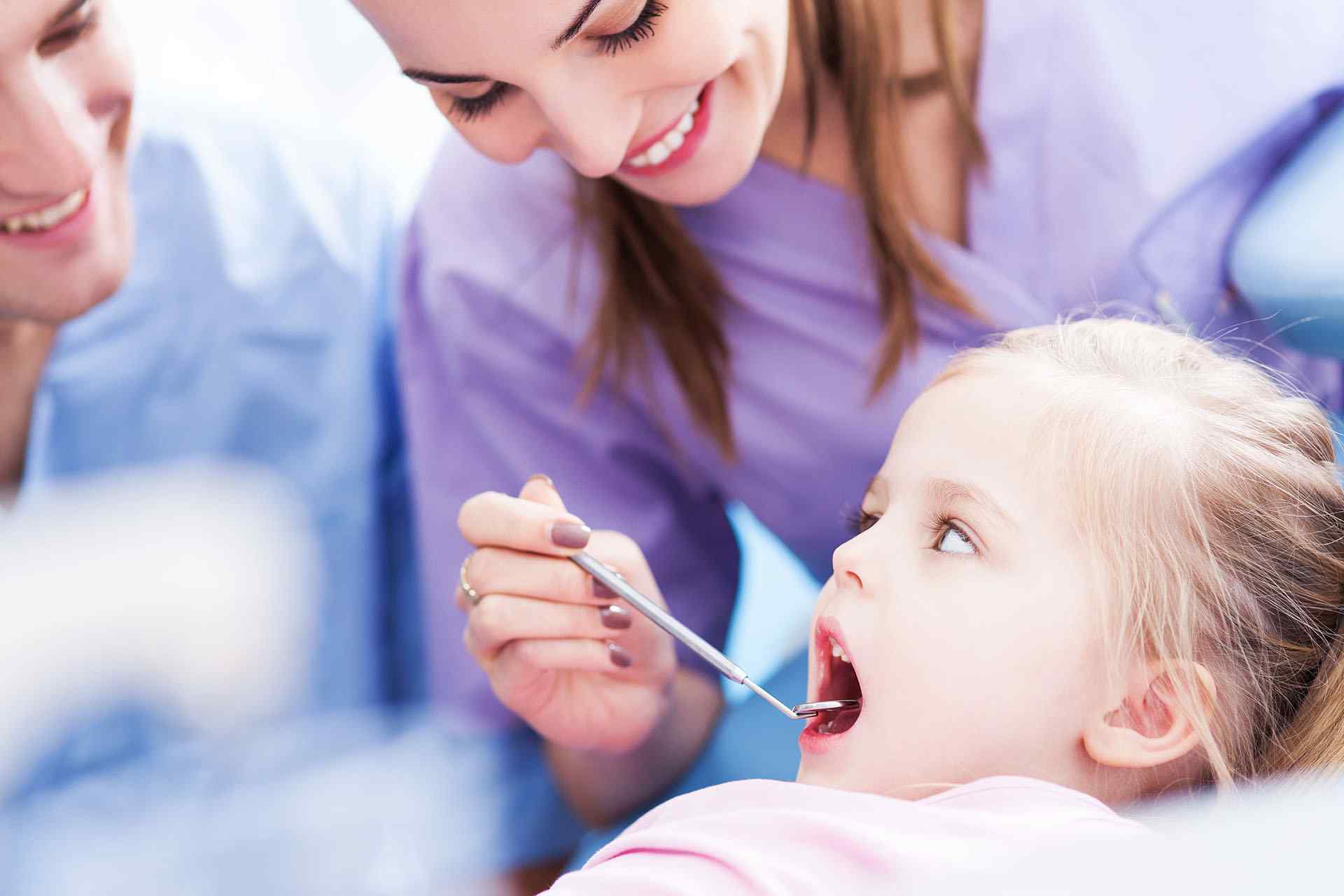
Pedodontics Treatments
Special approach to your children’s teeth, healthy teeth and smile with our pedodontics specialist.
Periodontics Treatments
Special approach to your children’s teeth, healthy teeth and smile with our pedodontics specialist.
Prosthetic Dental Treatments
Protective and aesthetic prosthetic applications for your damaged teeth.
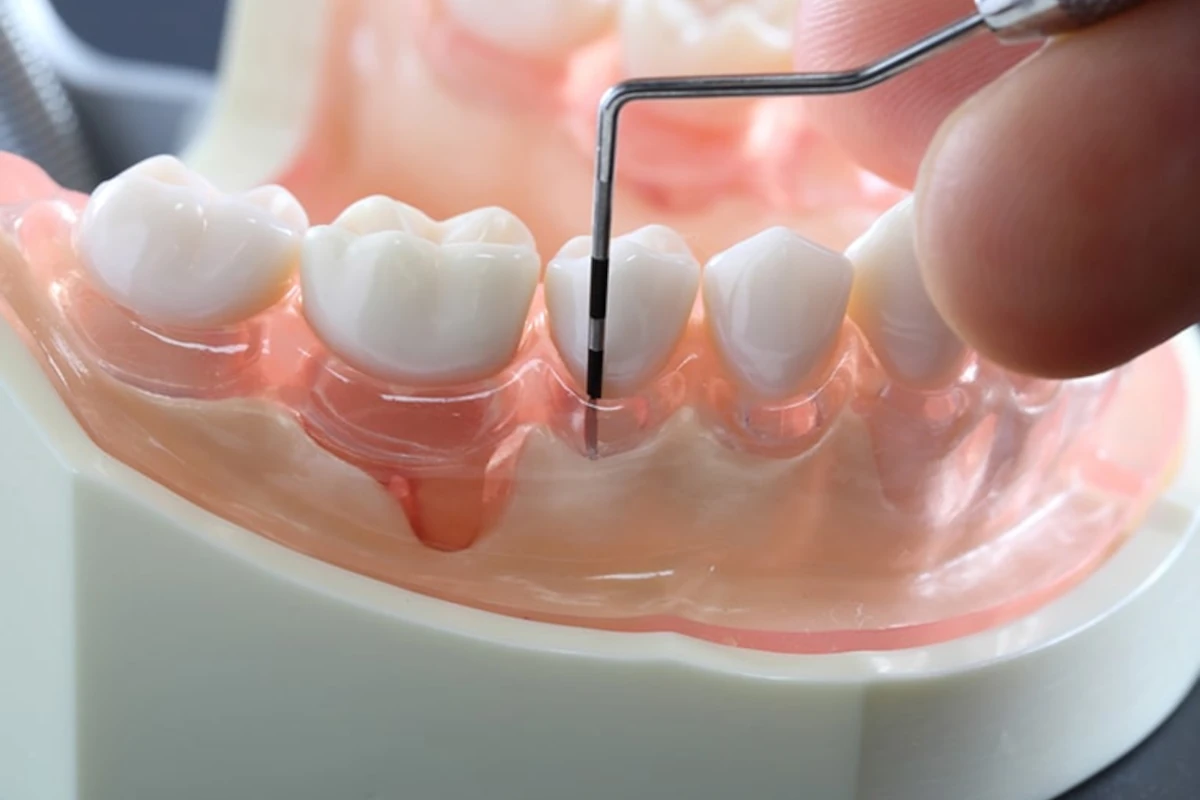
Restorative Dental Treatments
You are welcome to our clinic for procedures aimed at detecting and preventing decayed teeth.
Bahcesehir Dinamik Dental
Oral and Dental Health Polyclinic
You can reach us through our communication channels for special solutions for you with our team that does worthwhile work.